 Damping is the decrease in the amplitude of an oscillating system when its energy is drained out as heat energy.
Damping is the decrease in the amplitude of an oscillating system when its energy is drained out as heat energy. - The amplitude of an oscillating system will gradually decrease and become zero when the oscillation stops.
- Damping causes a decrease in amplitude and energy but the frequency of the oscillation remain unchanged.
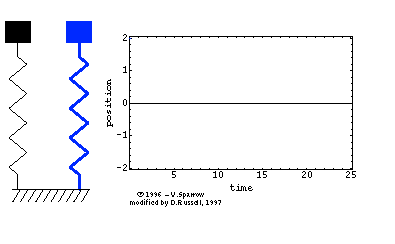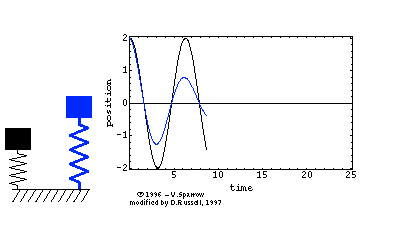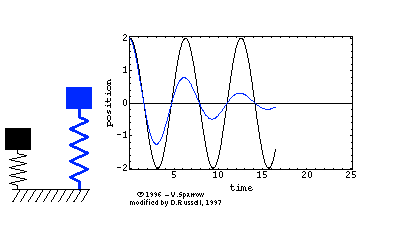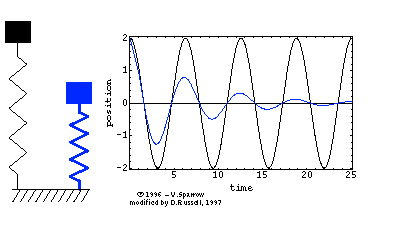
In the diagram on the right the blue spring is experiencing damping but not the black spring. take note of the decrease in amplitude but the frequency is the same. The initial amplitude was 2 unit and it was decreasing. But the frequency remains as 4 complete oscillations in 25 s (0.16 Hz).
There are two types of damping: External Damping and Internal Damping.
1. External Damping
- Is lost of energy to overcome frictional force or air resistance.
2. Internal Damping
- Is due to compression and extension of atoms and molecules of the system.
To enable an oscillating system to go on continuously, an external force must be applied to the system.
- The external force supplies energy to the system.
- Such a motion is called a forced oscillation.
The frequency of a system which oscillates freely without the action of an external force is called the natural frequency.
Application of damping in our daily lives
Vehicle suspension system. A vehicle spring and shock absorber system provides damping to prevent the vehicle from bouncing up and down continuously.

How car suspension work.
RESONANCE
- Occurs when a system/matter oscillate at a frequency equivalent to its natural frequency by an external force.
- Due to resonance, particle/matter oscillate at a higher amplitude.

In the Barton's pendulum on the right when pendulum X was oscillated it supplied energy to the other pendulums making them oscillate. It was observed that pendulum C oscillates with the largest amplitude. This is because pendulum X and pendulum C have the same pendulum length. The natural frequency of an oscillating system depends on its pendulum length. Therefore pendulum X and pendulum C are of the same natural frequency. Hence pendulum C is at resonance.
Video clip for Resonance
Good effects of Resonance in our daily lives
- A tuner in the radio or television enables you to select the channel we want. Te circuit in the tuner is adjusted until resonance is achieved, at the frequency transmitted by a particular station selected. Hence a strong electrical signal is produced.
- The loudness of a wind musical instrument like trumpet and flute is the result of resonance of the air.
Bad effects of Resonance in our daily lives
- A bridge may collapse when the amplitude of its vibration increases because of resonance. The action of the wind can cause the bridge to vibrate with a large amplitude as a result of resonance
- The loud explosion can cause a glass window to break
- The high pitch note of an opera singer can cause a thin glass to shatter






No comments:
Post a Comment